| Combo/Multi-Connector
Ethernet Boards |
| Combo/Multi-Connector
Ethernet Boards |
A wide selection of Ethernet cards offers more than one
connector, the boards can be used via a BNC-connector for Thin Ethernet
(10base2) or via an RJ-45 connector for Twisted Pair
Ethernet (10baseT/UTP) (some boards even offer a
connector for the 'original' Thick-Ethernet (10base5), which is now only used in large
networks to create Long-distance backbones.
First: although the card has 2 (or more) connectors, it has
only ONE set of electronics, so ONLY ONE
connector can be used (it is NOT possible to connect
BOTH a BNC/Coax cable and a RJ45/TP-cable and to communicate over both connected
network cables).
The question is now: is the
board 'smart' enough to work it out itself, in which of the plugs you connected
your cable ?
If the board needs to be configured,
but is NOT configured for the plug, where you have connected the network cable,
there will be no communication !
There are
quite a number of boards, where this is NOT configured automatically, but you as
the user have to define it.
1) Jumpers: some boards still used jumpers to define
port-address
and IRQ, and a few of
them have also a jumper defining, on which connector to use (some of the popular
NE2000 compatible boards have such jumpers).
Search for something like above, and set the jumper
properly.
2) Softset-boards: Some boards have no jumpers, but require to be configured via a
special software configuration utility. If you have such a "Soft-Set"
configurable board, have a look to see, if one of configuration parameters
define the connector to be used (I think, the 'original' INTEL EtherExpress requires
this type of configuration)
Example: 3COM Etherlink III
3C509B:
using the setup/diagnostic program 3C5X9CFG.EXE: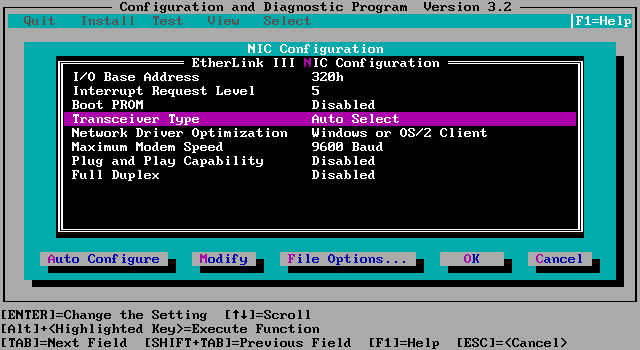
look for "Transceiver Type": on new
boards, the factory default should be "Auto Select" (so the board will detect
itself the type of connected network).
But when you get used boards, it may
have been pre-configured: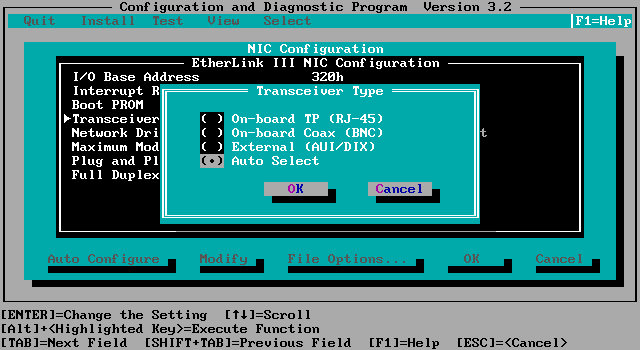
Put is then
back to "Auto-Select" or define your type of network cable.
3) Win95
adapter properties: Some boards (like the on-board AMD-network adapter on some older HP-models) are configured via the
"properties" of the "Network adapter", accessible from the "Network applet" in
the "Control-panel".
Example of an Intel Ether-Express: "Transceiver
Type:"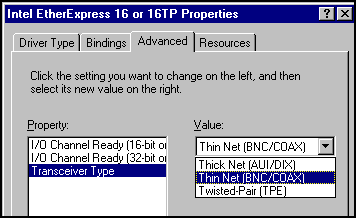
Example: 3COM Etherlink III PCMCIA 3C589:
Windows95: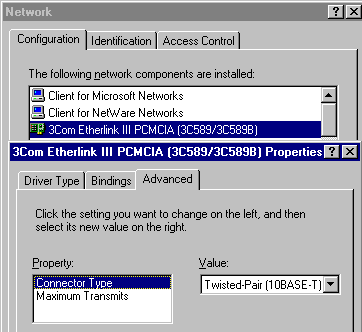 |
Windows NT4: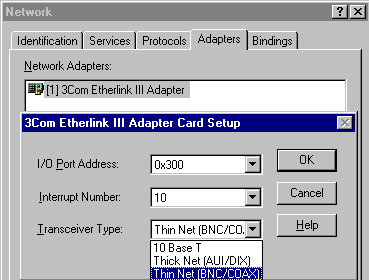 |